Geography
General information
Bordering Mauritania in the North, Mali in the East, Guinea and Guinea-Bissau in the South and the Atlantic Ocean in the West, Senegal occupies a surface of 196.712 km². Gambia forms an enclave within Senegal.
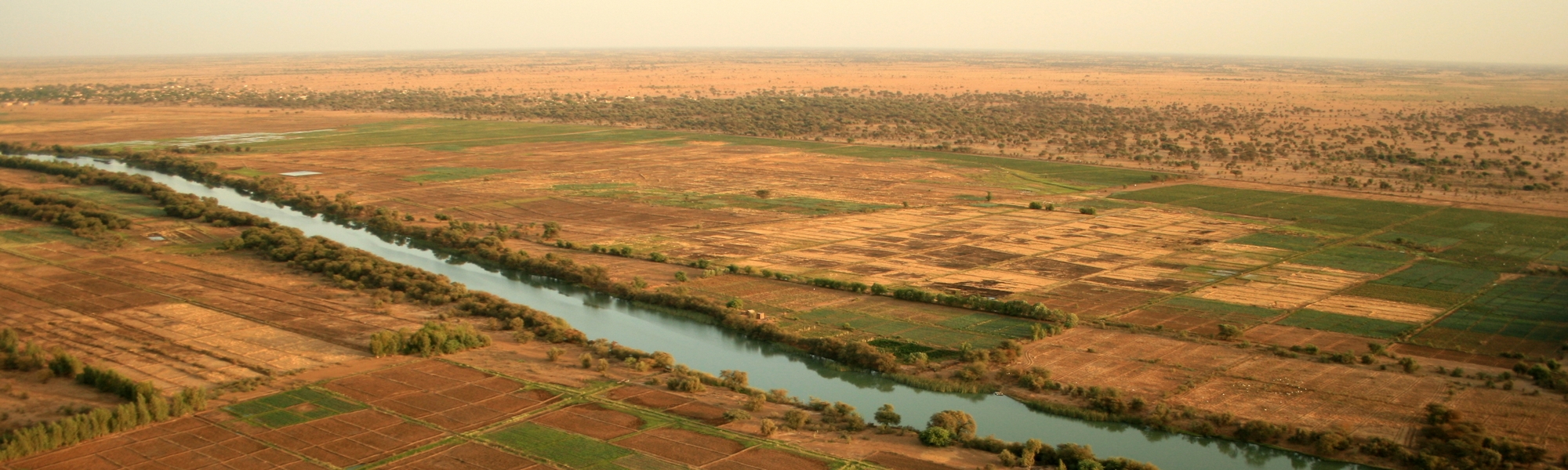
Thanks to its 1700km-long-river the natural border between Senegal and Mauritania is clearly drawn. From its source in Guinea, it also crosses Mali. The second river of the country is the river Gambia which runs through the Bassari region before joining its country. Let’s not forget the river Casamance and Sine Saloum, both in their respective region.
The territory is rather flat except for a few strategic spots like the Ferlo desert in the center and the Senegal river basin in the North of the country. There are also Les Mamelles in Dakar, two hills of about a hundred meters high, as well as the Bassari region, in East Senegal, which foresees the first slopes of the Fouta Djalon mountain massif.
8% of the territory of Senegal is composed of protected areas. The country has 6 national parks:
Many reserves and protected marine areas can also be found in the country. For instance: the Bandia Reserve, close to Saly, or the Guembeul Reserve next to Saint-Louis.
Climate
Climate in Senegal is diverse, with a desert region (Sahelian) in the North and a tropical region in the South. Two seasons are clearly distinguished:
- A dry season from November to May, with continental trade winds and mild temperatures
- A humid season from June to October (ironically called “wintering”), with higher temperatures and monsoon rains
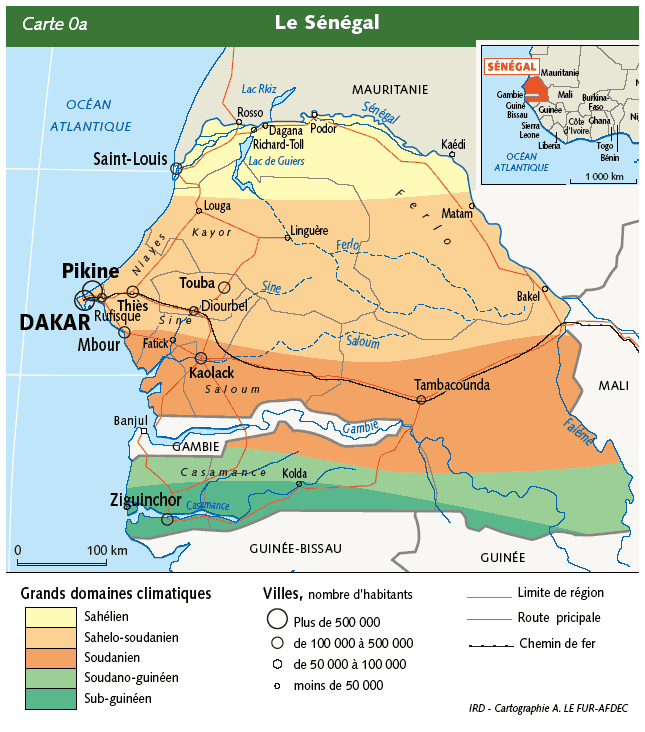
In the West, the coastline has cooler temperatures than in the East which remains, along with the center, the hottest place of the country. From North to South we can notice 5 large areas of tropical variation:
- The Sahelian area: between Saint-Louis and the River Senegal (desertification in progress, shrubs, some baobabs and acacias)
- The Sahelo-Sudanian area: from Dakar to Matam and from Louga to Djourbel (dry savannah, acacias, cheese trees, baobabs)
- The Sudanian area: from Fatick/Kaolack to Tambacounda (denser savannah, forests with sparse baobabs, cheese trees, acacias, palm trees)
- The Sudano-Guinean area: from Tambacounda to Ziguinchor/Kolda (very dense savannahs and forests with cheese trees, baobabs, palm trees, casuarinas,…)
- The Guinean area: South Casamance (humid tropical forest)
The temperature difference can be quite significant between the coastline and the interior of the country, by about 10 degrees; during the summer temperatures of more than 40° are recorded in the inland regions.